Must Know Linux Command that can make your Life Easier
The main intention of this article is to provide a basic understanding of Linux commands, you can learn more about them by using the man command man 'command name'
- Locate The locate command is used to locate files. Either a specific file can be searched or files with specific extensions can be searched as well.
-
The following command returns the entire path for the file "names.txt" if it exists on the machine. locate "name.txt"
-
The following command returns all the files that has the extension ".txt" locate "*.txt"
- Find Find is an important command which is used to find files or directories. So Locate command return the file location and the Find command return the file/directory name if it exists.
-
The following command return all the files in the current working directory(.). find .
-
The following command return all the directories in the current working directory. find . -type d
-
The following command returns all the files having the file extension ".txt" in the current working directory. -type f specifies that the type that should be searched is "file". -name ".txt" specifies that the name of the file that needs to be searched is everything() with the extension .txt . find . -type f -name "*.txt"
-
The following command returns all the files that are modified 20 minutes ago. find . -type f -mmin -20
-
The following command returns all the files that has a size more than 1Kb. find . -type f -size +1k
-
The following command returns all the files that has got read-write-execute permissions. find . -perm 777
- File Permissions Linux offers 3 permissions that can be assigned to all files and directories. There are 3 categories of owners for a file they are User(u) - Group(g) - Other(o). ls -l command displays all the files along with their permission details.
- Read(r/4) - Permission to open and read a file. The permission can be assigned either by specifying r or by using the number 4
In the following image you can see that the file test.txt is having read and write permission for User and read permission for both Groups and Others.
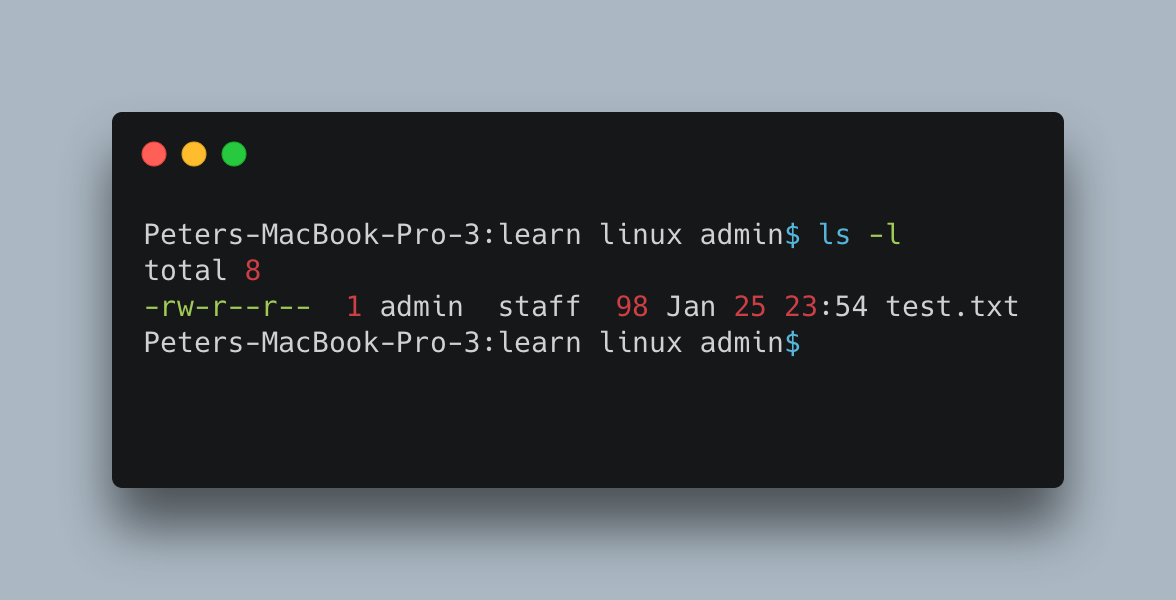
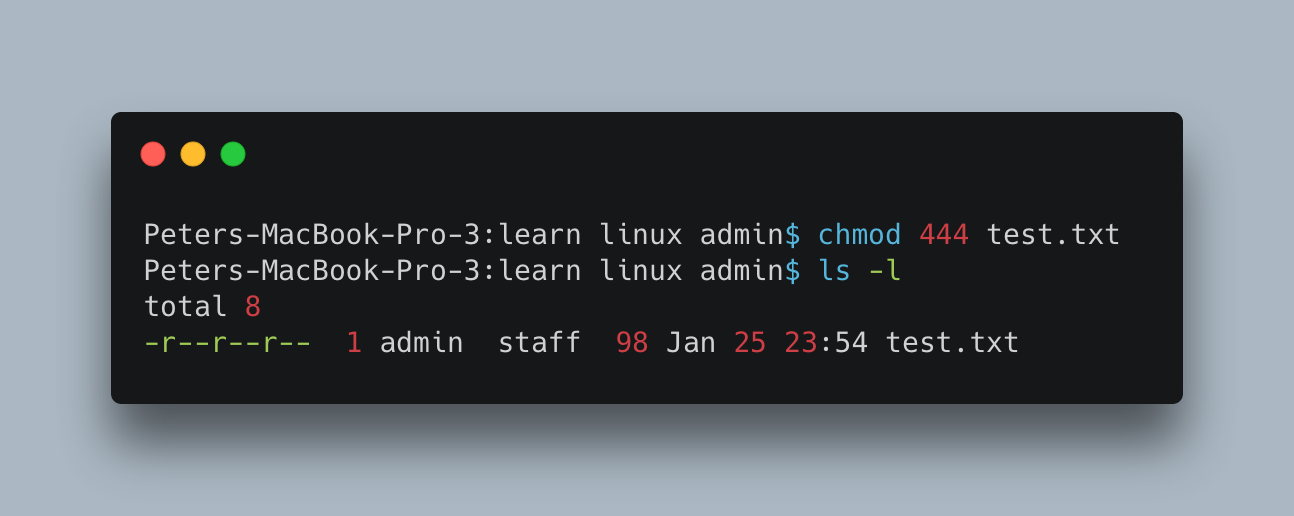
The following command sets the permission to read for all the owners. chmod 444 test.txt or chmod u=r,g=r,o=r test.txt
Output :
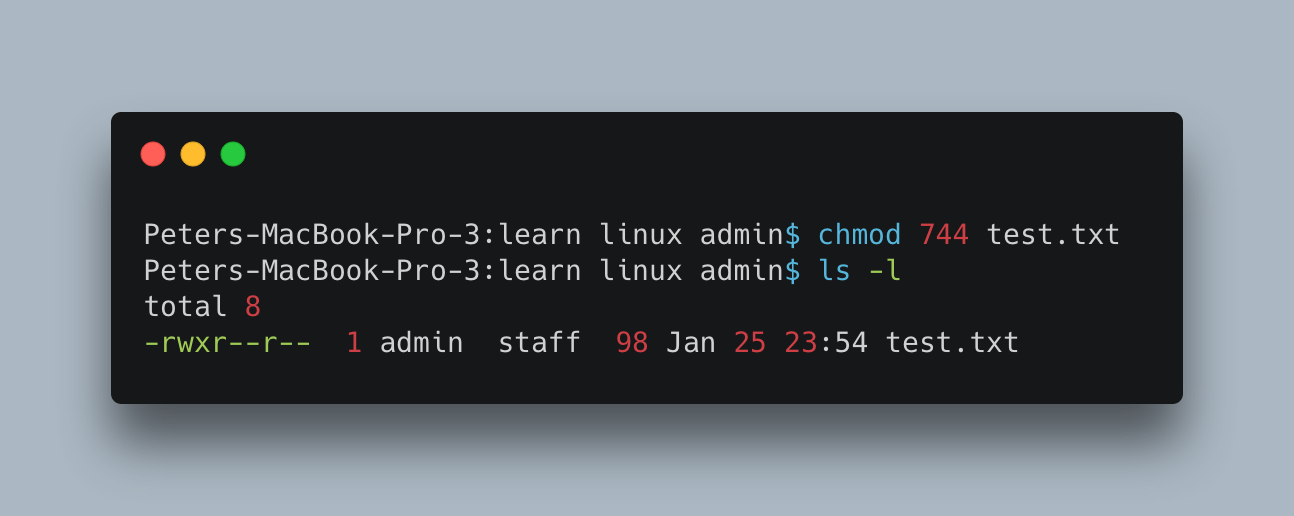
Another Example :
The following command sets the permission to read,write and execute for User and read to both Groups and Others
chmod 744 test.txt
Output :
- Write(w/2) : Permission to modify a file.
- Execute(e/1) : Permission to run a file.
- Perform an action on multiple files There can be situations where we need to perform an action to multiple files simultaneously in that case the find command which we discussed earlier comes in handy.
Example : In the following image you can see that there are 4 files and consider a situation in which we need to delete them in one go.
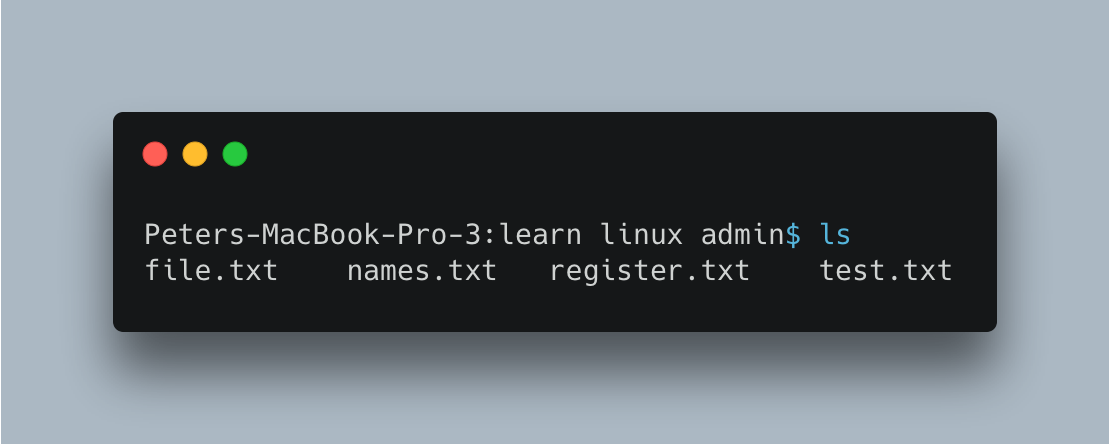
The following command selects all the files in the current directory("." : current directory, -type f : selects only file) and executes(-exec) the remove file command(rm -f). {} at first holds the first file file.txt then + selects the next file names.txt as + is mentioned and so on.. and for each file the command will be executed find . -type f -exec rm -f {} +
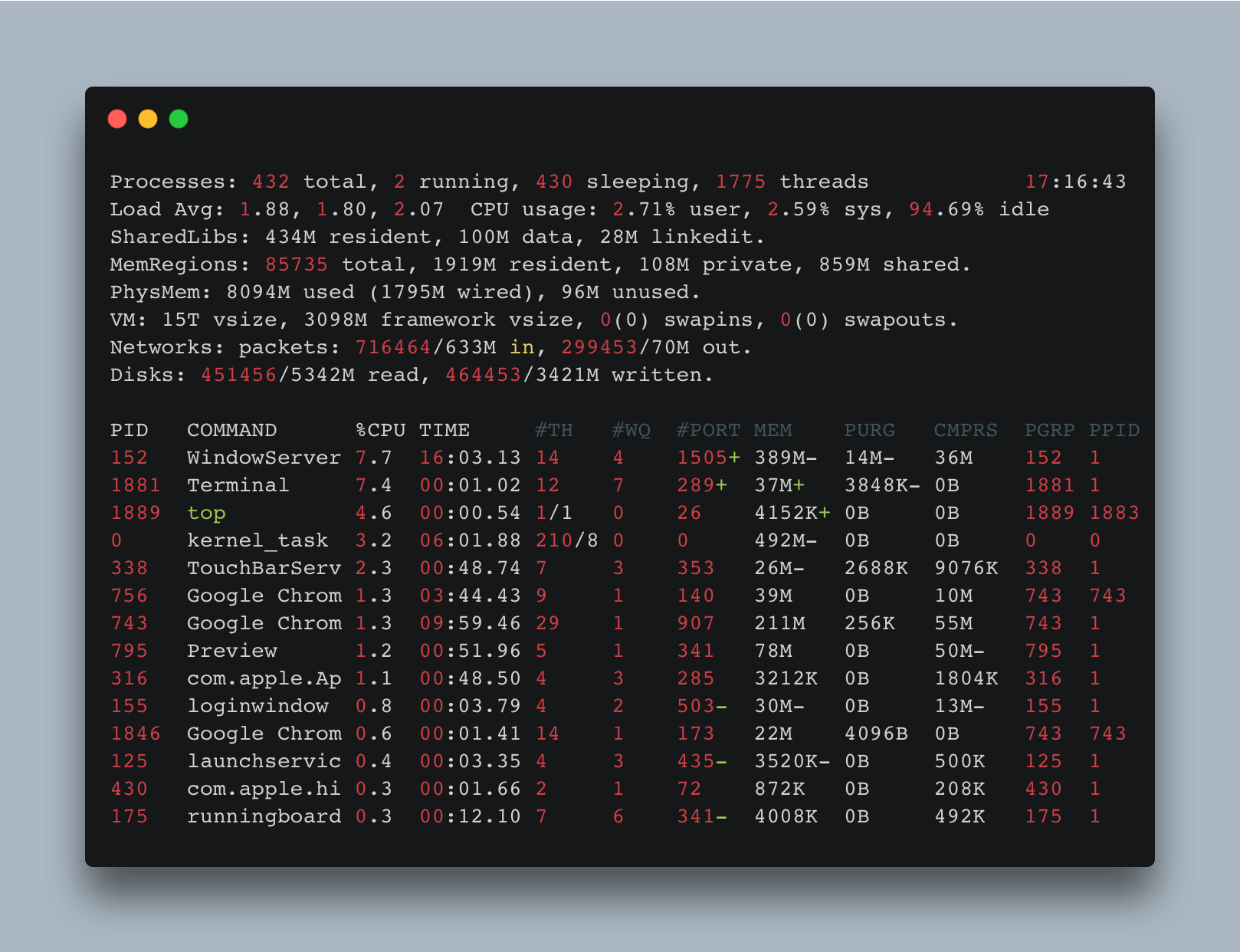
- top The top command displays all the processes that are running along with their PID,CPU usage,Time,Memory,Port Number etc.. The kill (PID) command can be used to kill a process, as the top command provides the PID of a process.
Output :

Hello and thanks for visiting! My name is Peter Johnson, and this is my website where I share intersting blogs around technology and finance.
Post Details
- Published on Jan 30, 2022
